Cosmetic packaging
Time: 2022-11-30 16:46:19
Background and penalties
Regulations on the Supervision and Administration of Cosmetics
Article 30 Cosmetic raw materials and packaging materials that directly contact cosmetics shall comply with mandatory national standards and technical specifications.
Do not use expired, discarded, recycled cosmetics or cosmetic raw materials to produce cosmetics.
Article 31 Cosmetics registrants, filers, and entrusted production enterprises shall establish and implement raw materials and packaging materials that directly contact cosmetics, inspection record system, and product sales record system. Purchase inspection records and product sales records shall be authentic, complete, and traceable, and shall be kept for no less than one year after the expiration of the product's service life; if the product's service life is less than one year, the records shall be kept for no less than two years.
Article 60 Under any of the following circumstances, the department in charge of drug supervision and management shall confiscate illegal income, cosmetics illegally produced and traded, and raw materials, packaging materials, tools, equipment and other items specially used for illegal production and trade ; If the value of cosmetics illegally produced and operated is less than 10,000 yuan, a fine of not less than 10,000 yuan but not more than 50,000 yuan will be imposed; If the circumstances are serious, the company shall be ordered to suspend production and business, the filing department shall cancel the filing or the original license issuing department shall revoke the cosmetics license, and the legal representative or main person in charge of the illegal unit, the directly responsible person in charge and other The person directly responsible shall be fined not less than one time but not more than three times the income obtained from the unit in the previous year, and shall be prohibited from engaging in cosmetics production and business activities within 10 years; if a crime is constituted, criminal responsibility shall be investigated according to law:
(1) Use of raw materials that do not meet mandatory national standards and technical specifications, or packaging materials that directly contact cosmetics

01 Supervision Status
Combining food safety management experience to ensure the safety of finished products.
The specific inspection specifications and standards for cosmetic packaging materials and the substances contained in them are mainly regulated in the national standards on packaging for the physical properties and characteristics of packaging. Among them, there are certain inspection standards for some migratory substances in food contact packaging materials, but there is no corresponding standard when it comes to cosmetics. It is worth noting that the past industry practice is that items not covered by cosmetic inspection can be implemented for drugs and food. Corresponding testing items, based on this, there are still gaps in the supervision of cosmetic packaging inspection. 【1】
Regulatory requirements include:
"Safety Technical Specifications for Cosmetics" (2015 Edition)
2 Terms and Definitions
2.17 Packaging materials: materials that directly contact cosmetic raw materials or packaging containers of cosmetics.
2.18 Safety Risk Substances: Substances produced or brought in by cosmetic raw materials, packaging materials, production, transportation and storage, which may cause potential harm to human health when exposed to the human body.
3 General Requirements for Cosmetics Safety
3.5 Packaging Material Requirements
Packaging materials that directly contact cosmetics should be safe, and must not chemically react with cosmetics, and must not migrate or release toxic and harmful substances that are harmful to the human body.
Prohibited component list note (1):
Prohibited ingredients in cosmetics include, but are not limited to, the substances in Table 1. The substances listed in Table 1 may exist in the finished product of cosmetics due to unintentional factors, such as impurities in natural or synthetic raw materials, packaging materials, or the production or storage of products.
Under the production conditions that comply with the national mandatory regulations, if the existence of prohibited components is technically unavoidable, the finished cosmetic product must meet the requirements that it will not cause harm to the human body under normal or reasonably foreseeable use conditions. requirements.
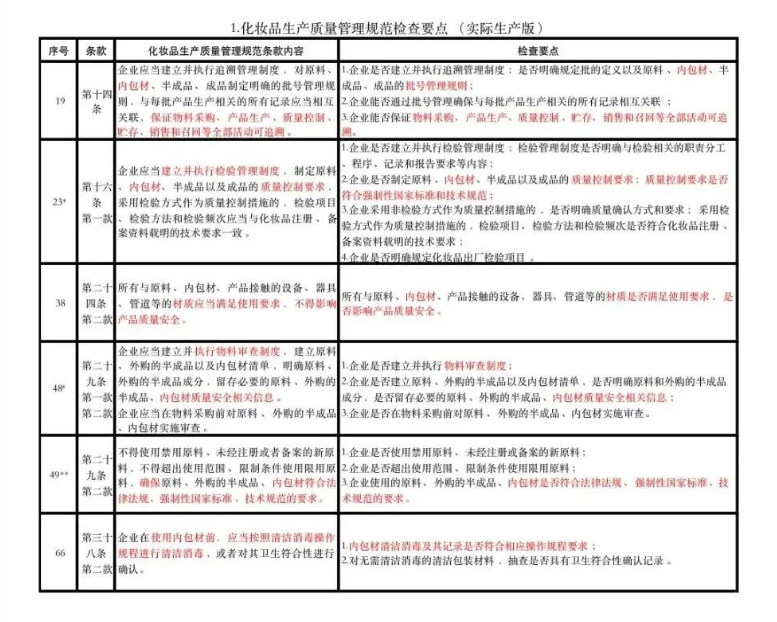
"Quality Management Standards for Cosmetic Production"
"Cosmetic production quality management specification inspection points"
Inner packaging material: refers to the packaging material that directly contacts the contents of cosmetics, and shall comply with the requirements of laws and regulations, mandatory national standards, and technical specifications.
SIMPLE LINES
02 Domestic and foreign research on the safety performance of cosmetic packaging materials
1. Domestic research status
Due to people's late attention to the safety performance of cosmetic packaging materials, there are still few domestic studies on the migration of cosmetic packaging materials. Guo Zhongshan et al. (2005) [24], referred to the standard of food packaging, randomly inspected 104 cases of cosmetic packaging in use, and the results showed that the rate of physical and chemical indicators exceeding the standard was 9.6%, and the precipitation of toxic substances in packaging materials into products did exist. Can not be ignored. Xiang Bin et al. (2011) took cosmetics (simulants) and plastic containers as research objects, and compared the relative indicators of potassium permanganate consumption, evaporation residue, migration of heavy metals, and decolorization experiments by setting different storage temperatures and times. To reveal the migration rule of precipitates between cosmetics and plastic containers. The test results show that the migration between oily cosmetics and plastic containers is relatively serious.
However, there are few reports on specific migration tests of substances in cosmetic packaging materials, and there are few reports on the specific migration of substances in food packaging materials and pharmaceutical packaging materials. Wang Zhenglin et al. (2007) used HPLC to study the migration of polyolefin antioxidants 1076 and 168 to edible blend oil, corn oil and rapeseed oil. The results showed that the type of oil had little effect on the migration process of antioxidants. It plays a decisive role in the migration kinetic process, and 100% ethanol can be used as a fat simulant to replace edible oil in the migration test of antioxidants; Zhao Weiwei (2007) determined the antioxidant 1076 and antioxidant 168 in n-hexane , isooctane and 95% ethanol immersion solution, and analyzed the stability of antioxidants, the results showed that the two antioxidants had good stability in n-hexane and isooctane, while the antioxidant The stability of oxygen agent 168 in 95% ethanol is relatively poor; Lin Qinbao et al. (2010) studied the migration of antioxidants in polyethylene film to isooctane, discussed the influence of temperature and time on migration, and Based on the migration data, a preliminary mathematical model was established; Wang Feng (2012) used HPLC method and ICP method to analyze the antioxidant 1010, antioxidant 168 and aluminum and magnesium in the hydrotalcite in the medicinal solution of the polypropylene infusion bottle. The amount of migration in was studied.
2. Current status of foreign research (EU and US regulations)
Cosmetic regulations in the European Union and the United States also seldom involve inspection standards for cosmetic packaging materials, but there are clear regulations that require cosmetic ingredient labels, and there is a list of prohibited and restricted substances for cosmetic prescription ingredients, which is also not clear Specify which requirements the packaging materials in direct contact need to meet. The European Union has issued a directive on impurities and industrial residues in chemical raw materials, including more than 1,300 banned substances, but it does not restrict the addition of substances in contact packaging materials in cosmetics. They mainly use the self-regulatory behavior of enterprises. aspects of supervision and management. In February 2012, the European Union directly listed three phthalates such as DEHP, DBP and BBP on the chemical elimination list, while the latest EU REACH stipulated that low-density polyethylene, polyethylene terephthalic acid, and cross-linked polyethylene Both vinyl chloride and vinyl chloride are not allowed to be used in finished products, which provide a direction for re-examining the packaging of plastics for cosmetics.
Compared with the lack of standards for cosmetic packaging materials, the European Union and the United States have a complete set of detailed food packaging and drug packaging regulations and standards. The European Union promulgated and implemented a framework directive in 1976: 76/893/EEC "Regulations on Food Contact Materials and Articles" [33], which makes the mandatory technical requirements of various countries in this field tend to be consistent. The Directive 82/711/EEC is 82/711/EEC for the basic rules of the migration test of materials and utensils in direct contact with food, which includes test objects, simulated liquids, test methods, test conditions, special circumstances, etc.
The Directive 85/572/EEC, which supplemented the simulants in 82/711/EEC, was promulgated three years later, which provides a detailed classification of foods, see Table 1.1[8]. Directive 89/109/EEC, which revised 76/893/EEC, is the second-generation framework directive for the EU to coordinate the legislation of food contact materials proposed by member states. The 2002/72/EEC promulgated in 2002 completely replaced 90/128/EEC, and at the same time gave the testing conditions for alternative fats.
The European Pharmacopoeia and the US Pharmacopoeia have material standards for pharmaceutical packaging materials, and they are divided into raw materials and products. The raw materials are divided into raw materials with additives and raw materials without additives. Similar to China's standards for direct contact drug packaging materials, this type of standard also has test items related to the migration of total substances in packaging materials, namely, dissolved matter tests, including test items such as clarity, easy oxidation, pH value, ultraviolet absorption, and heavy metals. It is used for preliminary evaluation of the safety performance of materials. In addition, there are special standards for detecting the migration of specific additives in packaging materials, such as EP7.0-3.1.6 "Polypropylene Containers for Parenteral and Ophthalmic Preparations" and so on. 【2】
03 Compatibility of packaging materials and migration of harmful substances
Migration of hazardous substances in packaging materials cannot be ignored!
Since domestic attention to the safety of cosmetic packaging materials has always been relatively small, there are few literatures on the migration of harmful substances in them. In 2005, Guo Zhongshan et al. conducted a random sampling test on cosmetic packaging in use with reference to food packaging standards. Among the 104 physical and chemical items tested, 10 cases of packaging bottles exceeded the standard, and the exceeding rate was 9.6%. This proves that harmful substances in packaging materials do migrate and the amount of migration cannot be ignored. In 2011, Cao Jin et al. reviewed the content of cosmetic packaging testing and inspection, pointed out the regulatory gap in this field, and proposed that the inspection of cosmetic packaging materials is one of the important contents of the future development of cosmetic inspection. In the same year, Liu Yangmei and others proved that certain substances contained in additives in plastics do have certain toxicity through the research and analysis of toxic and harmful substances that may migrate in cosmetic packaging plastics. Taking cosmetics and plastic packaging as research objects, Xiang Bin et al. compared the changes in the amount of precipitates at different times and storage temperatures to reveal the migration rules of precipitates between cosmetics and plastic packaging.
Glass packaging materials Be vigilant against the ingress of metal components and synthetic additives for rubber materials
my country's laws and regulations on glass packaging materials are mainly concentrated in the field of drugs and food, such as "Measures for the Administration of Packaging Materials and Containers in Direct Contact with Drugs" (State Food and Drug Administration Order No. 13), "Description of Chemical Drug Injections and Plastic Packaging Materials Technical Guidelines for Sexual Research (Trial)" (SFDA [2012] No. 267), "Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Quantitative Packaged Commodities" (Order No. 75 of the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine), "Management of Packaging and Labeling of Agricultural Products "Measures" (Decree No. 70 of the Ministry of Agriculture), "Administrative Measures for Export Commodity Transport Packaging Inspection (Trial)", etc., but there are very few laws and regulations on cosmetic packaging materials, and the research on the compatibility of cosmetic glass packaging materials is mainly Refer to the means and methods of testing medicines and food packaging.
Since glass bottles and jars need to add many additives in the production process, the following links should be paid attention to when testing the compatibility of glass packaging materials. First of all, the pH value, weather resistance, and the degree of shedding of the bottle body after shaking are detected; secondly, as cosmetic packaging materials, transparent glass products lack certain aesthetics, and Cu2O (to make transparent glass turn red), CuO ( make transparent glass blue-green), CdO (turn transparent glass yellow) and other metal substances [9] (see Figure 4), so it is necessary to detect the metal components that are imported into cosmetics; thirdly, rubber will be used in glass packaging materials Gaskets and seals of materials, rubber substances will add various additives during the synthesis process, so it is necessary to detect whether these additives have migrated into cosmetics.
Plastics Focus on testing the compatibility of plasticizers and packaging materials
In a broad sense, the compatibility of cosmetic packaging and its contents refers to the interaction between plastic packaging and cosmetics, including chemical compatibility, physical compatibility and biocompatibility. Taking PS resin and ABS resin as an example, if the reaction is not complete during the synthesis process, small molecular monomers such as styrene and vinyl chloride will remain and migrate into the content, causing further harm to the human body. For another example, one of the raw materials of PET resin is ethylene glycol. If the post-treatment is not in place during the reaction process, a certain amount of diethylene glycol will remain, and diethylene glycol can be mixed with water, and water is an indispensable ingredient in cosmetics. Therefore, cosmetics mixed with diethylene glycol are also harmful to the human body.
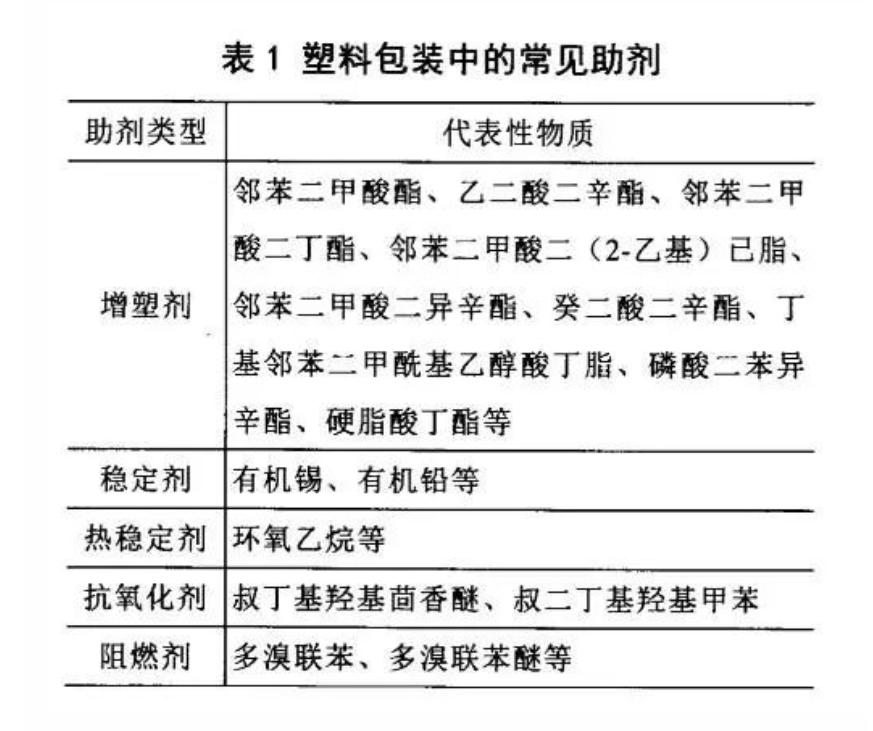
In recent years, with the continuous improvement of the synthesis technology of plastic packaging materials, these harmful substances produced during the polymerization and processing of polymer compounds have been controlled within the limit, and the harm to the human body is minimal, while the real harm to the human body is What hurts is the plasticizer in the plastic packaging material. In order to improve the plasticity of the resin, a certain amount of plasticizer must be added during the synthesis process to increase the ductility and flexibility of the plastic, so that the resin has excellent processing properties. The plasticizers used at this stage mainly include phthalates, anthracene oil, and phosphate esters. Phthalates are the most widely used plasticizers with the best plasticizing effect at this stage, but this kind of plasticizer has a great impact on human reproductive health, and has been strictly restricted and banned. Anthracene oil contains a large amount of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, which is physiologically toxic and has been restricted or banned. It can be seen that when studying the compatibility of plastic packaging materials, not only the migration of harmful substances should be considered, but also the compatibility between plasticizers and packaging materials should be tested. 【3-4】
SIMPLE LINES
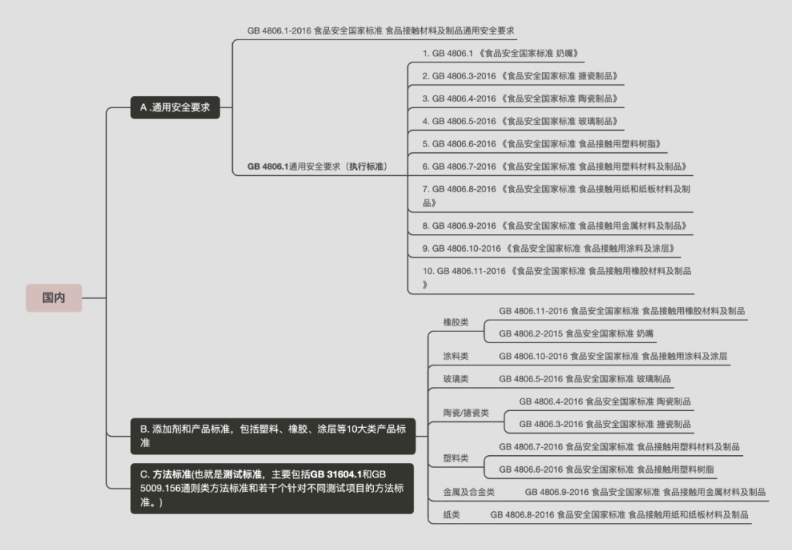
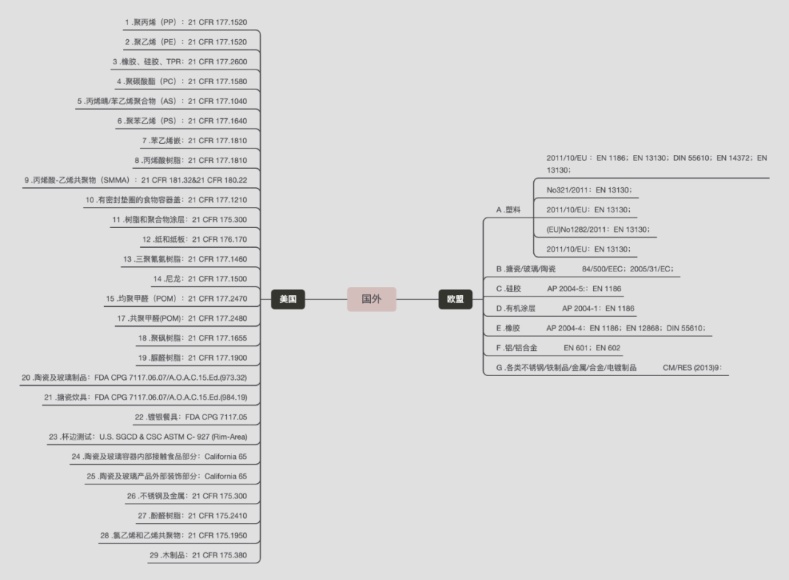
04 Standard system of food packaging materials at home and abroad